Where_Are_Japanese_Cars_Most_Popular_Around_the_World
Jul 18,2025
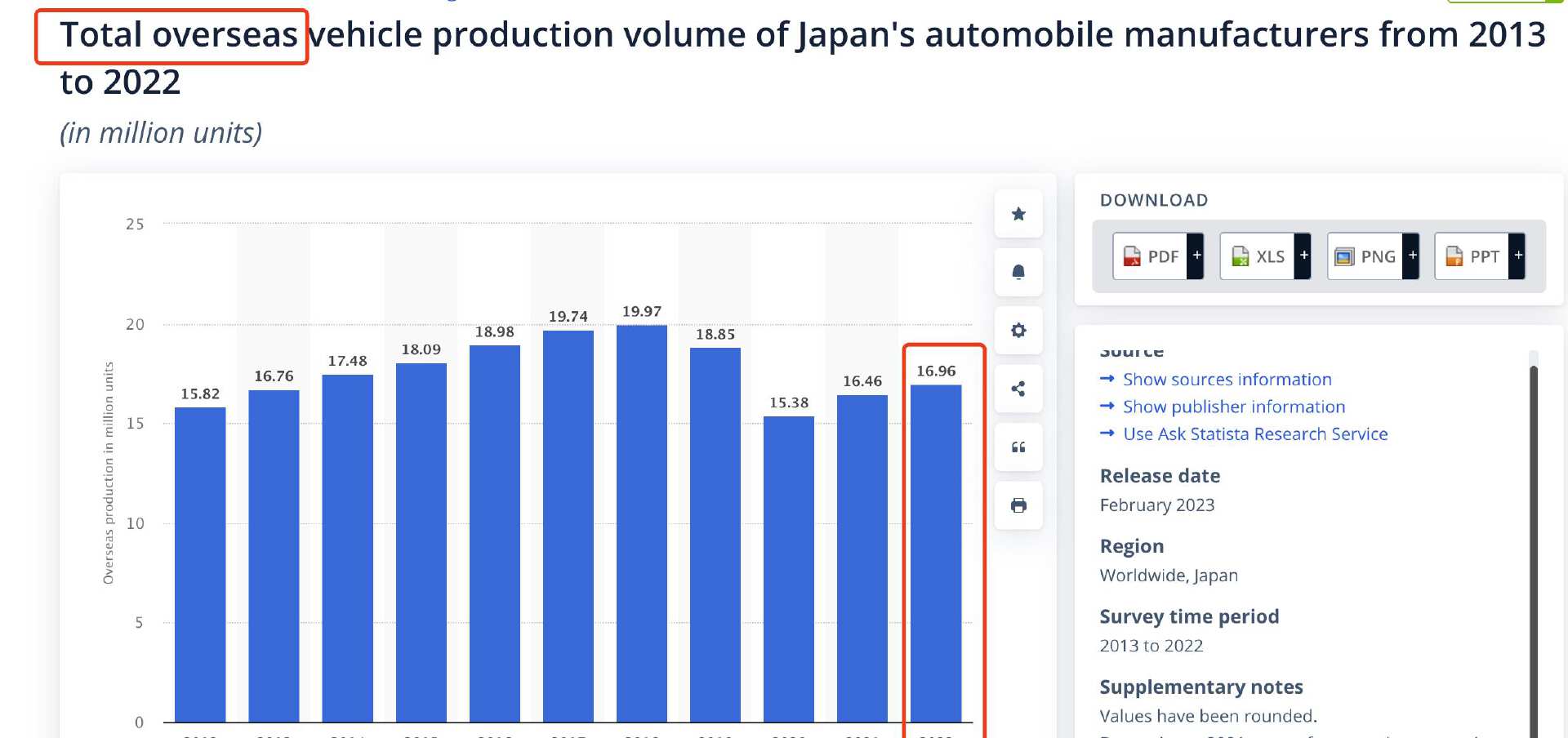
In 2022, approximately 23.53 million Japanese-brand vehicles were produced worldwide, including 6.57 million units domestically in Japan and 16.96 million units overseas. This accounts for about 27.7% of the global production and sales volume of 85.02 million vehicles.
Notably, Japan represents only 1.6% of the world’s population, which partly explains how the country—despite being resource-poor, frequently affected by natural disasters, facing one of the world’s most severe aging populations, and experiencing a "lost three decades" of economic stagnation—continues to hold its position among developed nations. The automotive industry remains a key pillar supporting Japan’s economic stability.

Domestic Japan: 93%
Japanese-brand vehicles have consistently held over 90% market share within Japan. In 2022, the top eight best-selling automotive brands in the Japanese market were all Japanese manufacturers: Toyota, Suzuki, Daihatsu, Honda, Nissan, Mazda, Subaru, and Mitsubishi.

9th Place: Mercedes-Benz is the Best-Selling Imported Brand in Japan
In 2022, Mercedes-Benz sold 52,000 units in Japan, outperforming even Lexus. Following Mercedes, Volkswagen ranked 13th with 33,000 units sold, and BMW came 14th with 30,000 units.
Why do over 90% of Japanese consumers buy domestic vehicles despite Japan’s zero import tariffs?
There are three main reasons:
- Japan’s uniquely critical K-Car market—a segment of small, lightweight vehicles—is largely ignored by foreign brands due to its niche size and special requirements.
- Japanese automakers produce high-quality vehicles that deeply understand and meet local market needs.
- Although import tariffs are zero, entering the Japanese market involves complicated certification procedures. For brands with relatively low sales, the costs of certification and marketing can outweigh profits.
Additionally, historically when Japanese automakers were less advanced, the government implemented stringent protectionist policies favoring domestic brands, cultivating consumer habits that favor local manufacturers.
2. Southeast Asia: 76%
Southeast Asia is often called the “backyard of Japanese cars,” with Japanese brands accounting for 76% of new vehicle sales. Of these, 6% are produced in Japan, while 70% are manufactured or assembled in key Southeast Asian countries such as Thailand, Malaysia, and Indonesia.
The dominance of Japanese vehicles in Southeast Asia is largely due to their early and dedicated market entry. Japanese automakers have tailored many models specifically for this region. For example, the Honda BR-V—a compact SUV only 4.4 meters long—can accommodate seven passengers. This design suits Southeast Asia’s narrow roads and limited parking spaces, as well as the region’s larger family sizes that require seven-seat vehicles.

Despite this, domestic Chinese brands are rapidly making inroads into the Southeast Asian market. For example, Geely is selling cars in Malaysia through its joint venture with Proton. Additionally, manufacturers like Great Wall Motors and MG have established factories in Thailand and have already achieved notable success. In the compact SUV segment during Q1 2023 in Thailand, the Haval H6 ranked first with a market share as high as 46.6%. In the electric vehicle market, BYD took the lead in April 2023 with 1,734 units sold, capturing a 46.6% share.
3. India: 44%
Although India’s population size is comparable to China’s, its automotive market was only 3.78 million vehicles in 2022, roughly one-sixth the size of China’s passenger vehicle sales of 20 million.
Maruti Suzuki was the top-selling brand in India in 2022, moving 1.576 million units and commanding a dominant 41.7% market share.

Given the volatility of India’s business environment, lessons from major investors like South Korea’s Daewoo, and U.S. automakers General Motors and Ford—who have suffered substantial losses there—highlight the need for cautious investment. Xiaomi’s approximately $4.7 billion in assets being frozen further underscores this risk.
However, domestic brand MG still holds a foothold in India, selling 4,551 units in April 2023 and totaling 18,900 units from January to April, ranking eighth in the market.

4. Middle East: 39%
The Middle Eastern automotive market has an annual scale of roughly 1.2 million units, with Japanese brands accounting for nearly 40% of sales. Of these, 13% are imported from Japan, and 26% are produced locally within the region. For example, in the UAE in 2020, Toyota led with a 36.6% market share, followed by Nissan-Renault at 23.2%, and Mitsubishi at 9.2%. These top three Japanese brands together hold 69% of the market.

This region also presents strong opportunities for domestic Chinese brands to gain market share. Brands like Great Wall, Geely, and MG have already made significant progress. In the UAE, MG sold about 6,100 new vehicles in 2022—a year-over-year increase of over 100%—ranking eighth among all brands, up from 14th place in 2021, reflecting rapid growth.

In another major Middle Eastern market, Israel, BYD’s Atto 3 (Yuan PLUS) led sales in Q1 2023 with 5,602 units, Geely Geometry C ranked third, and Chery Tiggo 8 Pro was sixth. Chery’s internal combustion vehicles have been steadily cultivated in Israel, and thanks to strong government incentives favoring electric vehicles—purchase tax on gasoline cars is 83% versus just 20% on EVs—Geely and BYD have made rapid gains.
Currently, over a dozen Chinese brands have entered the Israeli market, including MG, Ora, Great Wall’s WEY and Lynk & Co, as well as emerging players like Skyworth, Voyah, and Leapmotor.

Finally, in Egypt—the most populous country in the Middle East—Chery and BYD ranked second and third respectively in Q1 2023, capturing market shares of 18.3% and 9.6%. Chinese brands now account for one-third of Egypt’s new vehicle market.
5. North America: 38%
Japanese brands hold a total market share of 38% in North America, with 9% imported directly from Japan and 29% produced locally.

Taking the U.S. market as an example, among the top ten best-selling brands from January to May 2023 (excluding Tesla), six are Japanese. By corporate group, Toyota and Lexus combined outsold Ford, ranking first overall. Honda, Subaru, and Mazda also perform well in the U.S.
However, the U.S. market structure is well established. While electric vehicles offer a potential breakthrough, qualifying for the $7,500 subsidy under the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) is highly restrictive. This makes it very challenging for Chinese automakers to enter the U.S. market directly, though there may be opportunities to enter indirectly through manufacturing and supply chain operations in Mexico.
6. South America: 20%
Japanese vehicles account for 20% of the South American market, with 3% imported from Japan and 17% produced locally.
The South American automotive market sells between 4 to 6.3 million vehicles annually, with major markets including Brazil, Argentina, Chile, and Colombia. Despite strong potential, high vehicle prices limit demand. For example, a Toyota RAV4 in Brazil costs approximately 322,890 Brazilian Reais (about 456,000 RMB).

This high price is mainly due to substantial taxes and tariffs; for instance, Brazil and Argentina impose import duties as high as 35%. To succeed in South America, manufacturers often need to build local plants and focus on new energy vehicles. Most Japanese vehicle sales in the region are from locally produced units.
Some automakers have already established factories in South America. Chery opened a plant in Brazil in 2014 and sold 7,830 vehicles there from January to May, with some exports to Argentina. BYD sold 393 new vehicles in Brazil in May, primarily the Song PLUS DM-i plug-in hybrid. Because it is a PHEV, import tariffs range from 0-7%, depending on electric fuel consumption and driving range.
7. China: 17%
Japanese brands hold a total market share of 17% in China, with 1% imported from Japan and 16% produced locally.
However, starting in 2023, sales have begun to sharply decline. In Q1 2023, Toyota, Honda, and Nissan experienced year-on-year drops of 14.5%, 37.7%, and 36.8% respectively, while Mazda’s sales plunged by 66.1%.

Toyota has managed to maintain relatively stable sales largely through significant discounts—even the Highlander is now discounted by over 20,000 RMB, which was previously unheard of. As new energy vehicles (NEVs) surpass a 35% penetration rate in China, Japanese automakers have begun introducing NEV models such as Nissan’s N7. However, ongoing reform and innovation are necessary; otherwise, their market share could fall below 10% within a few years.
8. Europe: 13%
Japanese brands account for 13% of the European market, with 4% imported from Japan and 9% produced locally. For example, Toyota operates eight production facilities in Europe.
The recent surge in Japanese vehicle sales in Europe is mainly driven by the popularity of hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs). Toyota’s European sales reached 1.081 million units in 2022, a 0.9% increase despite an overall European auto market decline of 11%. Toyota’s market share rose to 7.3%, with electrified vehicles (including HEVs) accounting for as much as 66% of sales.

However, significantly increasing Japanese market share further in Europe remains challenging. Most European subsidies favor pure electric vehicles, and local automakers remain highly competitive. Products like the Toyota bZ4X alone are insufficient; innovation in the new energy electric vehicle segment remains critical.
Contact Us




